The Definitive Guide to Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Measurement
Why Measure H2S?
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) is a naturally occurring gas found in crude oil, natural gas, volcanic gases and hot springs. It can also be generated by the bacterial breakdown of organic matter, the processing of municipal wastewater, as well as a multitude of manufacturing and industrial processes. Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless gas with a distinctive foul odor of rotten eggs. Depending on the concentration, H2S gas can be toxic to humans, corrosive to metals and flammable. The measurement of H2S levels is important for both the safety of personnel and the integrity of industrial process equipment, infrastructure and pipelines.
Industries Measuring H2S
Continuous monitoring of an atmosphere is required when there is a high likelihood of hydrogen sulfide gas being present. This is often within enclosed environments, such as mines, wastewater treatment plants, construction excavations, sewers, or other confined spaces. The primary purpose for monitoring is to protect human health, prevent accidental ignition of the gas or detect emissions that could cause foul odors for surrounding communities. Atmospheric concentrations exceeding 100 ppm are immediately harmful to human health, while lower concentrations can cause irritation. Area monitoring for H2S is achieved with electronic samplers that can be fixed, portable or personally mounted. All monitors will sound an alarm if H2S is detected above preset levels, which alerts personnel to take corrective action or move to safety.
Hydrogen sulfide is also found naturally within natural gas fields, and its concentrations can vary from parts per million to percentage levels. H2S must be monitored and often removed from natural gas to meet regulatory and commercial requirements. Natural gas that contains in excess of 4ppm H2S is commonly referred to as ‘sour gas’. Within natural gas, H2S is monitored to ensure tariff limits are met at receipt, sales, and interconnection points throughout the system or to verify process specifications are maintained within gas processing plants. H2S levels of 0-20 ppm are quite common within transmission pipelines and can be significantly higher at wellheads and within gathering systems.
H2S Measurement Technologies
Here are a few of the common methods for H2S measurements:
Electrochemical | Electrochemical based H2S sensors measure the concentration of the gas by an oxidation reaction of the H2S that generates a current flow proportional to the gas concentration. These sensors are very accurate and repeatable with the ability to detect trace levels of H2S. Additionally, their small size make them an excellent choice for H2S analyzers. Certain non-target gasses can interfere with the sensor measurement and must be considered. | Pros:
| Cons:
|
Stain Tubes | Stain tubes can provide an approximate measurement for H2S in natural gas or other process gasses. A stain tube contains lead acetate or copper sulphate that reacts with the hydrogen sulfide. The gas sample is drawn into the stain tube with a hand pump, and the color change of the lead acetate is proportional to the H2S concentration. There are multiple factors that can affect the accuracy of the reading, including atmospheric conditions, gas composition and the operator’s technique for drawing the sample. | Pros:
| Cons:
|
Lead Acetate Tape | H2S tape analyzers utilize a lead acetate-coated tape to detect the presence of H2S in a gas sample. When the tape is exposed to the gas sample it develops a brown stain proportional to the H2S concentration. A detector is used to measure the amount of staining on the tape. Tape analyzers can measure low levels of H2S repeatably, but this comes with a high initial cost. Ongoing maintenance of consumables and many moving parts can also be a concern. | Pros:
| Cons:
|
Tunable Diode Laser (TDL) | Tunable diode lasers are commonly used in gas streams to measure the concentrations of the constituents of the gas. The technology utilizes the absorption characteristics of different gases to measure the concentration of a target gas. A detector measures the intensity of the laser light energy after it passes through the gas sample to determine the target gas concentration. A properly engineered TDL analyzer can provide accurate and extremely reliable measurements at very low levels of H2S. Because the gas stream never makes contact with the laser or detector, the measurement systems in not impacted by contaminants or corrosive gasses. There are no calibration or regular maintenance requirements. | Pros:
| Cons:
|
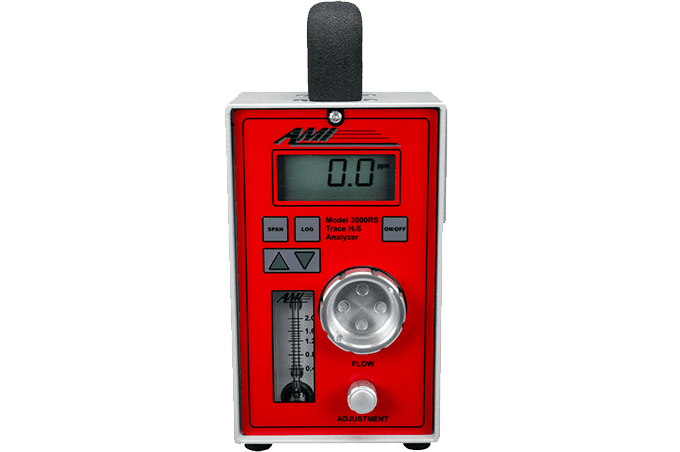
Advantages of the Electrochemical H2S Analyzer
Electrochemical H2S Analyzers provide users with accurate measurements, the option for either unattended monitoring or spot-checking and a low price point – all in a single compact footprint.

Accurate Measurements
Some H2S measurement methods rely on subjective interpretation to arrive at a reading. This means that the reading can vary substantially and depends a lot on the person performing the measurement. In situations involving trace measurements, subjective readings can result in errors as high as +20%.
The measurement produced by an electrochemical H2S Analyzer is entirely objective and extremely accurate because the Analyzer utilizes a sensor, consisting of an anode and cathode in an aqueous electrolyte solution. If H2S molecules are present in the sample gas as it passes through the sensor, electrons will flow from the anode to the cathode and produce an electric current. The size of the current is proportional to the number of electrons moving to the cathode and is used by the Analyzer to derive the H2S reading. This precision of this method allows the Analyzer to handle applications that require trace measurements that go as low as the parts per billion – something that should not be left to manual subjective methods such as stain tubes.
Permanent Mount & Portable Configurations
Electrochemical sensor technology can be used in the design of both permanent mount and portable H2S Analyzers. This flexibility allows users to adopt one technology platform from a single manufacturer to carry out their measurements. It reduces the learning curve and makes it easier for all employees to use and operate both permanent and portable H2S Analyzers if their application needs it.

Cost-effective Solution
The value of the electrochemical H2S Analyzer is very compelling when you consider all ongoing costs required for other measurement options. A single-use stain tube is priced much lower than the Analyzer, but the overall cost spikes after many months of usage. Combined with the labor requirements, the stain tube option can exceed the cost for purchasing a single electrochemical Analyzer in months. Lead acetate tape Analyzers are also an option for users. However, they cost more than an electrochemical H2S Analyzer during the initial purchase, and their maintenance costs, which can be very unpredictable, are higher as well.

Required Maintenance
Periodic maintenance is required by most H2S Analyzers, and some procedures are easier to complete than others. For example, operators of lead acetate tape analyzers must check the condition of moving parts and, if necessary, change out worn-out components or depleted consumables. In contrast, the maintenance for an electrochemical Analyzers is relatively easy and mostly requires replacing an expired H2S sensor. Therefore, when considering any H2S Analyzer, be sure to weigh maintenance requirements as part of your purchase decision.